| python使用xpath(超详细) | 您所在的位置:网站首页 › pycharm etree › python使用xpath(超详细) |
python使用xpath(超详细)
|
使用时先安装 lxml 包 开始使用和beautifulsoup类似,首先我们需要得到一个文档树 把文本转换成一个文档树对象 from lxml import etree if __name__ == '__main__': doc=''' first item second item third item fourth item fifth item # 注意,此处缺少一个 闭合标签 ''' html = etree.HTML(doc) result = etree.tostring(html) print(str(result,'utf-8')) 把文件转换成一个文档树对象 from lxml import etree # 读取外部文件 index.html html = etree.parse('./index.html') result = etree.tostring(html, pretty_print=True) #pretty_print=True 会格式化输出 print(result)均会打印出文档内容 节点、元素、属性、内容xpath 的思想是通过 路径表达 去寻找节点。节点包括元素,属性,和内容 元素举例 html ---> ... div ---> ... a ---> ...这里我们可以看到,这里的元素和html中的标签一个意思。单独的元素是无法表达一个路径的,所以单独的元素不能独立使用 路径表达式 / 根节点,节点分隔符, // 任意位置 . 当前节点 .. 父级节点 @ 属性 通配符 * 任意元素 @* 任意属性 node() 任意子节点(元素,属性,内容) 谓语使用中括号来限定元素,称为谓语 //a[n] n为大于零的整数,代表子元素排在第n个位置的元素 //a[last()] last() 代表子元素排在最后个位置的元素 //a[last()-] 和上面同理,代表倒数第二个 //a[position()2] price值大于2的元素 多个路径用| 连接两个表达式,可以进行 或匹配 //book/title | //book/price 函数xpath内置很多函数。更多函数查看https://www.w3school.com.cn/xpath/xpath_functions.asp contains(string1,string2) starts-with(string1,string2) ends-with(string1,string2) #不支持 upper-case(string) #不支持 text() last() position() node()可以看到last()也是个函数,在前面我们在谓语中已经提到过了 案例 定位元素匹配多个元素,返回列表 from lxml import etree if __name__ == '__main__': doc=''' first item second item third item fourth item fifth item # 注意,此处缺少一个 闭合标签 ''' html = etree.HTML(doc) print(html.xpath("//li")) print(html.xpath("//p"))【结果为】 [, , , , ] [] #没找到p元素 html = etree.HTML(doc) print(etree.tostring(html.xpath("//li[@class='item-inactive']")[0])) print(html.xpath("//li[@class='item-inactive']")[0].text) print(html.xpath("//li[@class='item-inactive']/a")[0].text) print(html.xpath("//li[@class='item-inactive']/a/text()")) print(html.xpath("//li[@class='item-inactive']/..")) print(html.xpath("//li[@class='item-inactive']/../li[@class='item-0']"))【结果为】 b'third item\n ' None #因为第三个li下面没有直接text,None third item # ['third item'] [] [, ] 使用函数 contains有的时候,class作为选择条件的时候不合适@class='....' 这个是完全匹配,当网页样式发生变化时,class或许会增加或减少像active的class。用contains就能很方便 from lxml import etree if __name__ == '__main__': doc='''first item second item third item fourth item fifth item # 注意,此处缺少一个 闭合标签 ''' html = etree.HTML(doc) print(html.xpath("//*[contains(@class,'item')]"))【结果为】 [, , , , ] starts-with from lxml import etree if __name__ == '__main__': doc='''first item second item third item fourth item fifth item # 注意,此处缺少一个 闭合标签 ''' html = etree.HTML(doc) print(html.xpath("//*[contains(@class,'item')]")) print(html.xpath("//*[starts-with(@class,'ul')]"))【结果为】 [, , , , , ] [] ends-with print(html.xpath("//*[ends-with(@class,'ul')]"))【结果为】 Traceback (most recent call last): File "F:/OneDrive/pprojects/shoes-show-spider/test/xp5_test.py", line 18, in print(html.xpath("//*[ends-with(@class,'ul')]")) File "src\lxml\etree.pyx", line 1582, in lxml.etree._Element.xpath File "src\lxml\xpath.pxi", line 305, in lxml.etree.XPathElementEvaluator.__call__ File "src\lxml\xpath.pxi", line 225, in lxml.etree._XPathEvaluatorBase._handle_result lxml.etree.XPathEvalError: Unregistered function看来python的lxml并不支持有的xpath函数列表 upper-case和ends-with函数一样,也不支持。同样报错lxml.etree.XPathEvalError: Unregistered function print(html.xpath("//a[contains(upper-case(@class),'ITEM-INACTIVE')]")) text、last #最后一个li被限定了 print(html.xpath("//li[last()]/a/text()")) #会得到所有的``元素的内容,因为每个标签都是各自父元素的最后一个元素。 #本来每个li就只有一个子元素,所以都是最后一个 print(html.xpath("//li/a[last()]/text()")) print(html.xpath("//li/a[contains(text(),'third')]"))【结果为】 ['fifth item'] ['second item', 'third item', 'fourth item', 'fifth item'] [] position print(html.xpath("//li[position()=2]/a/text()")) #结果为['third item']上面这个例子我们之前以及讲解过了 *这里有个疑问,就是position()函数能不能像text()那样用呢 print(html.xpath("//li[last()]/a/position()")) #结果 lxml.etree.XPathEvalError: Unregistered function这里我们得到一个结论,函数不是随意放在哪里都能得到自己想要的结果 node返回所有子节点,不管这个子节点是什么类型(熟悉,元素,内容) print(html.xpath("//ul/li[@class='item-inactive']/node()")) print(html.xpath("//ul/node()"))【结果为】 [] ['\n ', , '\n ', , '\n ', , '\n ', , '\n ', , ' 闭合标签\n '] 获取内容刚刚已经提到过,可以使用.text和text()的方式来获取元素的内容 from lxml import etree if __name__ == '__main__': doc=''' first item second item third item fourth item fifth item # 注意,此处缺少一个 闭合标签 ''' html = etree.XML(doc) print(html.xpath("//a/text()")) print(html.xpath("//a")[0].text) print(html.xpath("//ul")[0].text) print(len(html.xpath("//ul")[0].text)) print(html.xpath("//ul/text()"))【结果为】 ['first item', 'second item', 'third item', 'fourth item', 'fifth item'] first item 18 ['\n ', '\n ', '\n ', '\n ', '\n ', ' 闭合标签\n ']看到这里,我们观察到text()和.text的区别。自己总结吧。不太好表达,就不表达了 获取属性 print(html.xpath("//a/@href")) print(html.xpath("//li/@class"))【结果为】 ['link1.html', 'link2.html', 'link3.html', 'link4.html', 'link5.html'] ['item-0 active', 'item-1', 'item-inactive', 'item-1', 'item-0'] 自定义函数我们从使用函数的过程中得到结论,就是有的函数不支持,有的支持,那问题来了,到底哪些函数支持呢。我们在lxml官网找到了答案。https://lxml.de/xpathxslt.html。lxml 支持XPath 1.0 ,想使用其他扩展,使用libxml2,和libxslt的标准兼容的方式。XPath 1.0官方文档 以及其他版本的XPath文档 https://www.w3.org/TR/xpath/ lxml supports XPath 1.0, XSLT 1.0 and the EXSLT extensions through libxml2 and libxslt in a standards compliant way.除此之外,lxml还提供了自定义函数的方式来扩展xpath的支持度 https://lxml.de/extensions.html from lxml import etree #定义函数 def ends_with(context,s1,s2): return s1[0].endswith(s2) if __name__ == '__main__': doc=''' first item second item third item fourth item fifth item # 注意,此处缺少一个 闭合标签 ''' html = etree.XML(doc) ns = etree.FunctionNamespace(None) ns['ends-with'] = ends_with #将ends_with方法注册到方法命名空间中 print(html.xpath("//li[ends-with(@class,'active')]")) print(html.xpath("//li[ends-with(@class,'active')]/a/text()"))【结果为】 [, ] ['first item', 'third item'] 形参s1会传入xpath中的第一个参数@class,但这里注意@class是个列表 形参s2会传入xpath中的第二个参数'active','active'是个字符串官网例子https://lxml.de/extensions.html def hello(context, a): return "Hello %s" % a from lxml import etree ns = etree.FunctionNamespace(None) ns['hello'] = hello root = etree.XML('Haegar') print(root.xpath("hello('Dr. Falken')")) # 结果为 Hello Dr. Falken xpath1.0支持的函数列表 number last() 谓语中返回在兄弟元素中排在最末尾的 number position() 谓语中,返回该元素在兄弟中的排名 number count(node-set) 返回子节点的个数 ,node-set代表子节点的表达式 //*[count(@*)=1] 属性只有一个的元素(因为元素的属性本身就是子节点) //*[count(*)=1] 任意一种属性如果为1,就满足 //*[count(a)=1] 子元素中有一个``的元素 node-set id("foo") 返回唯一id为foo的元素 。尝试了多次,未尝试出来,这里的唯一id是基于xml的,有下面这样一句话。所以确实没测试出来 If a document does not have a DTD, then no element in the document will have a unique ID.string local-name(node-set?) string name(node-set?) string namespace-uri(node-set?) string concat(string, string, string*) boolean starts-with(string, string) boolean contains(string, string) string substring-before(string, string) string substring-after(string, string) string substring(string, number, number?) number string-length(string?) string normalize-space(string?) number sum(node-set) number floor(number) number ceiling(number) number round(number) xpath使用工具 chome生成xpath表达式经常使用chome的小伙伴的都应该知道这个功能,在 审查 状态下(快捷键ctrl+shift+i,F12),定位到元素(快捷键ctrl+shift+c) ,在Elements选项卡中,右键元素 Copy->Copy xpath,就能得到该元素的xpath了
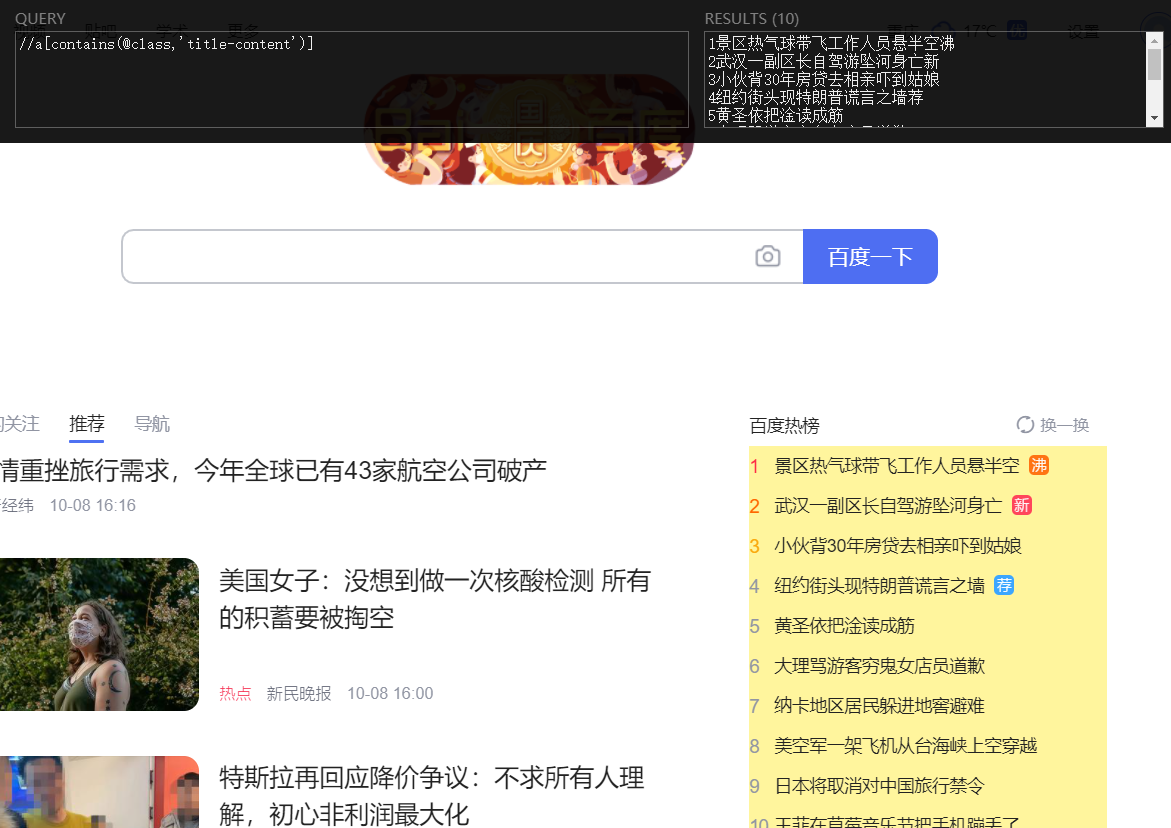
为chome装上XPath Helper就可以很轻松的检验自己的xpath是否正确了。安装插件需要kxsw(使用lanternFQ,或者Astar VPN),安装好插件后,在chrome右上角点插件的图标,调出插件的黑色界面,编辑好xpath表达式,表达式选中的元素被标记为黄色
|
【本文地址】
| 今日新闻 |
| 推荐新闻 |
| 专题文章 |